The sarcoplasmic reticulum SR is a membrane-bound structure found within muscle cells that is similar to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum in other cellsThe main function of the SR is to store calcium ions Ca 2Calcium ion levels are kept relatively constant with the concentration of calcium ions within a cell being 10000 times smaller than the concentration of calcium ions outside the. 50 organic functional groups.
Caffeine Molecular Structure Good Morning Chemical Formula Coffee Inspiration Motivation Symbol Vector Line Illustration Isolated On White Stock Vector Image Art Alamy

What Is Caffeine Structure Side Effects Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
![]()
Caffeine Icon Molecular Structure With Coffee Vector Image
76 reactions of naphthalene 12-dioxygenase.

Caffeine molecular structure. Recommend you check it out. Just as the 20th century was marked by the development of electricity telephones aviation computing and private motor vehicles the 21st century will be marked by significant progress in a broad spectrum of technologies among them. The metabolism of Caffeine can be increased when combined with Rifampicin.
Caffeine and adenosine have a similar molecular structure. So when caffeine is present in the brain it competes with adenosine to bind to the same receptors. Adenosine Receptors Tocris Bioscience 2793.
For example every water molecule contains two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. It has practically no stimulant effect on the central nervous system. Many of the products we use every day are the result of distillation from the gasoline that powers our cars to the water we drink.
All but one. Caffeine is a naturally occurring stimulant that can be isolated from over sixty plants but can also be made synthetically and added to our everyday food products and medication. Caffeine is a central nervous system CNS stimulant of the methylxanthine class.
There are several known mechanisms of action to explain the effects of caffeine. They compose a rich support system that is essential to the operation of nervous tissue and the nervous system. Unlike neurons glial cells do not have axons dendrites or conduct nerve impulsesNeuroglia are typically smaller than neurons and are about three times more numerous in the nervous system.
Caffeine is a naturally occurring stimulant that can be isolated from over sixty plants but can also be made synthetically and added to our everyday food products and medications. Upon ingestion caffeine binds to adenosine receptors in the central nervous system CNS which inhibits. The model shows hydrogen atoms white Nitrogen atoms blue Carbon atoms green and oxygen atoms red bonded together.
For example common variants of the gene encoding for the A2a receptor can disrupt sleep or cause anxiety in some individuals after ingesting caffeine. The ratio of the numbers of atoms that can be bonded together to form molecules is fixed. A1 and A2B antagonist.
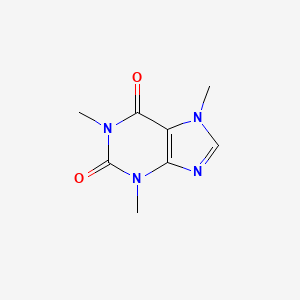
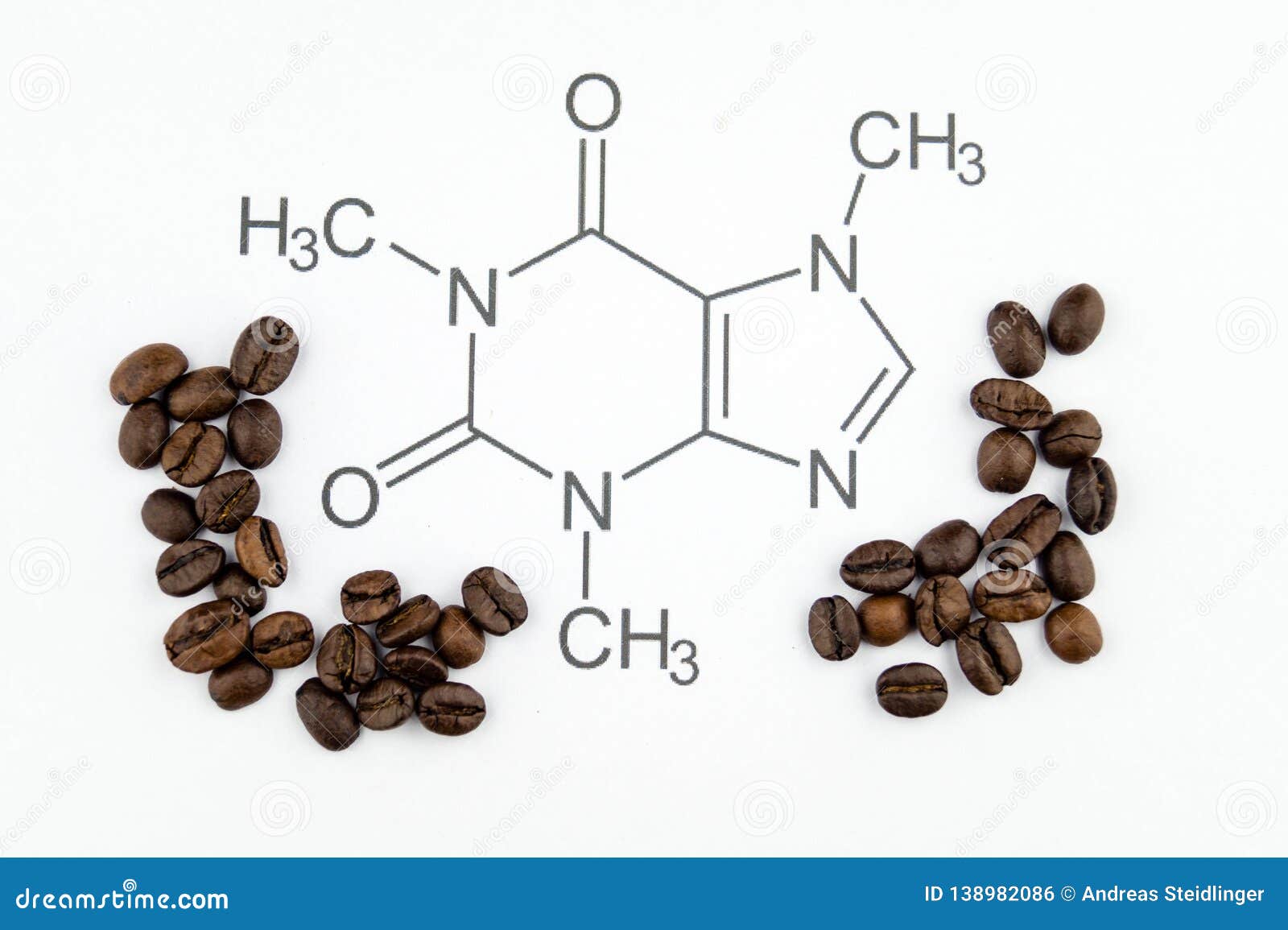
And Other Graphics Metapathway and Pathway Maps and Reaction Mechanisms. Caffeines chemical name is 137-triemthlxanthine based on its formula C 8 H 10 N 4 O 2 and molecular structure. A xanthine alkaloid that is used as a bronchodilator and as a vasodilator.
Lists of 219 pathways. Jiaogulan is not stimulating like Mate or coffee but has many interesting benefits. Neuroglia also called glia or glial cells are non-neuronal cells of the nervous system.
Thats what Im interested in. I have shown the relationship between molecular structure and absorption spectra. Caffeine a demethylated methyl donor - theophylline a.
First it may be that the molecular structure is just different enough not to trigger the caffeine allergy. Why then does the peak wavelength tend to be shifted toward the long wavelength region as the size of the conjugated system increases. As to the gentleman who found he is allergic to caffeine but not to mateine I have two speculations.
It is the worlds most widely consumed psychoactive drug. Molecular computing genomics rational drug design and alternative energy. 109 reactions of toluene dioxygenase.
It would be easy to state that his headaches are a result of his anger until you consider the fact that he drinks more beverages containing caffeine and sleeps less than six hours a night on average when he is angry. Distillation is a physical process that uses heat to purify or separate mixtures containing one or more liquids. Let us consider the relationship between the energy of.
However caffeine doesnt slow the. Having a 1-azacycloalkan-2-one structure or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. The molecular targets of caffeine namely the adenosine receptors also have great genetic variability.
The figure above is the 3D molecular structure of caffeine. Structurally caffeine and the other methylxanthines resembles the purines. It has a weaker diuretic activity than theophylline and is also a less powerful stimulant of smooth muscle.
The molecular structure of synthetic caffeine is apparently nearly indistinguishable from natural caffeine chemical compound but is there nothing left of the processing chemicals in that final product. In pure form it is a bitter white powder. Unlike many other psychoactive substances it is legal and unregulated in nearly all parts of the world.
Thus hydrogen and oxygen may be present in any arbitrary proportions in mechanical mixtures but. As a mixture is. CNS stimulant Tocris Bioscience 2793.
Caffeine 137-trimethylxanthine is a plant alkaloid with a chemical structure of C 8 H 10 N 4 O 2 see Figure 21 and a molecular weight of 19419. Molecular Framework Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds External Descriptors N-methylpiperazine. Theobromine 37-dimethylxanthine is the principle alkaloid in Theobroma cacao the cacao bean and other plants.
Caffeine is a methylxanthine alkaloid found in the seeds nuts or leaves of a number of plants native to South America and East Asia that is structurally related to adenosine and acts primarily as an adenosine receptor antagonist with psychotropic and anti-inflammatory activities. Caffeines chemical name is 137-trimethylxanthine based on its formula C 8 H 10 N 4 O 2 and molecular structure. Knowing precisely how all this plays out at the molecular level will help us and others create better ways to control the role of these two receptors in itchiness and other conditions Roth said.
Zerenex Molecular ZBioX-0453 Biochemicals small moleculesAntagonists inhibitors Hello Bio HB2846. Caffeine - 137-trimethylurate PlantCyc 1-3-7-TRIMETHYLXANTHINE. Of the nitrogen atoms are trigonal planar meaning they have 3 substituents around the atom.
7-TM Receptors Tocris Bioscience 2793. An example of how an uncontrolled variable can alter the results of an experiment is when a person gets angry he gets a severe headache. It is this feature that distinguishes chemical compounds from solutions and other mechanical mixtures.
1
Caffeine Molecule Structure Stock Photo Image Of Health Drawing 138982086
/caffeine-molecule--computer-artwork-showing-the-structure-of-a-molecule-of-the-alkaloid-stimulant-and-legal-drug-caffeine--caffeine-is-found-in-drinks-such-as-tea--coffee--and-fizzy-drinks--it-is-also-found-in-chocolate--536232214-59aeb9e622fa3a0011c0d2b9.jpg)
What Is Caffeine And How Does It Work

Caffeine Molecule Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

Caffeine Formula Structure
Caffeine C8h10n4o2 Pubchem

Caffeine Structure Stock Illustrations 687 Caffeine Structure Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime

File Caffeine Svg Wikimedia Commons